RepoDb, a hybrid-ORM library for .NET - Part I
RepoDb, a hybrid-ORM library for .NET - Part I
อย่างที่เราทราบกันดีว่าการเข้าถึงฐานข้อมูลมีส่วนสำคัญในการพัฒนาผลิตภัณฑ์และซอฟต์แวร์ และเป็นส่วนที่สำคัญที่สุดอย่างหนึ่งของการใช้งาน เนื่องจากจำเป็นต้องได้รับการออกแบบมาเป็นอย่างดีเพื่อให้สามารถเปลี่ยนแปลงได้ง่าย
ด้วยเหตุนี้ การใช้ object relational mapping (ORM) จึงเข้ามามีบทบาท เป็นพื้นฐานทั่วไปสำหรับนักพัฒนาส่วนใหญ่เมื่อพูดถึงการเข้าถึงข้อมูล ไลบรารี ORM ช่วยลดความซับซ้อนและทำให้การนำข้อมูลใน Database ไปใช้งานง่ายขึ้น และในขณะเดียวกันก็ช่วยให้การพัฒนาเร็วขึ้น มันทำงานในส่วนที่ซับซ้อนไปพร้อมกันในขณะที่เราใช้มัน แต่แน่นอนว่าเราควรทราบ “ข้อดี” และ “ข้อเสีย” ของการใช้ ORM ในแอปพลิเคชันของเราด้วย
ปัจจุบันโลกของ C# (หรือ .NET โดยรวม) มีไลบรารี ORM จำนวนมากในตลาด ทั้งแบบโอเพ่นซอร์สและเชิงพาณิชย์ เฟรมเวิร์กที่ได้รับความนิยมมากที่สุดคือ Entity Framework (เฟรมเวิร์กจาก Microsoft) นอกจากนี้ยังมีส่วนอื่นๆ เช่น NHibernate, Dapper (micro-ORM จาก StackOverflow) และ LLBLGen Pro
ด้วยเหตุนี้เอง เราในฐานะนักพัฒนาจึงมีหน้าที่เลือกสิ่งที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับความต้องการของเราเพราะเราต้องคำนึงถึง เวลาในการพัฒนา ความเรียบง่าย ประสิทธิภาพ ฯลฯ
ทำไมต้อง RepoDb ??
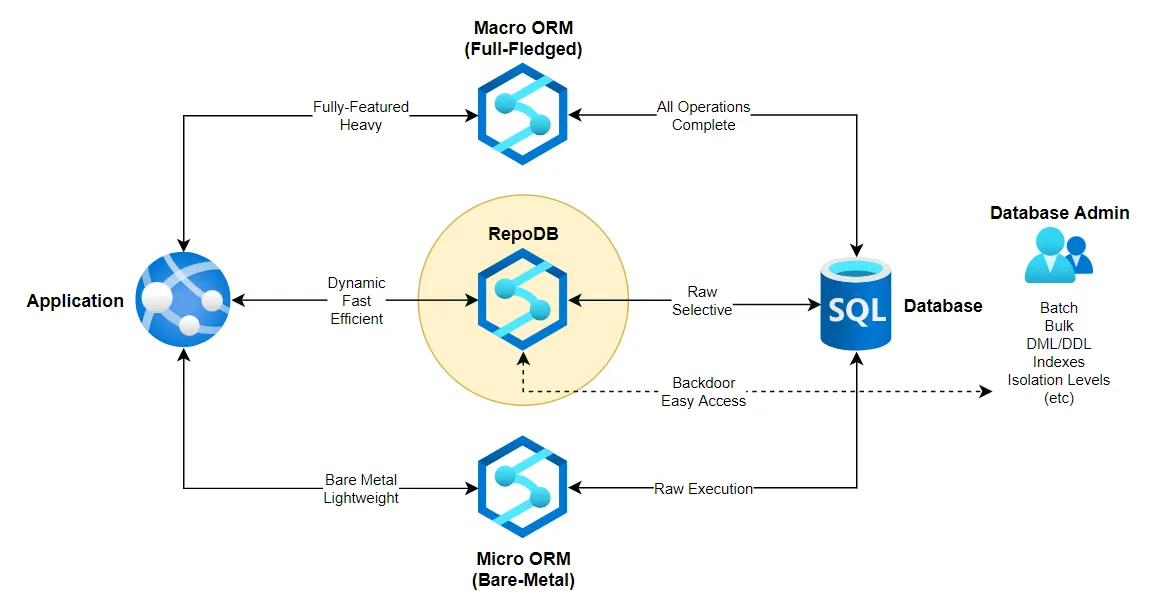
 เป็นไลบรารี ORM แบบไฮบริดแบบไดนามิก ที่เบา(lightweight),มีสมรรถภาพ และมีประสิทธิภาพ(high-performance) สูงสำหรับ .NET
เป็นไลบรารี ORM แบบไฮบริดแบบไดนามิก ที่เบา(lightweight),มีสมรรถภาพ และมีประสิทธิภาพ(high-performance) สูงสำหรับ .NET
- คำว่า “สมรรถภาพ” หมายถึง “ความเร็ว” ORM นี้จะแปลงข้อมูลดิบเป็นอ็อบเจ็กต์คลาส และขนส่งอ็อบเจ็กต์คลาสเป็นข้อมูลจริงในฐานข้อมูล
- คำว่า “มีประสิทธิภาพ” หมายถึง “การจัดการที่ดี” ORM นี้ใช้หน่วยความจำคอมพิวเตอร์เมื่อจัดการกับวัตถุตลอดการใช้งาน (cycle of the process.)
เราจะเรียก RepoDb ว่า hybrid-ORM ก็พราะว่ามันมีความสามารถที่ micro-ORM และ full-ORM มีในการที่มันทำให้เกิดความยืดหยุ่นแก่นักพัฒนาในการทำให้งานเกี่ยวกับ Database
ไลบรารีนี้รองรับคุณสมบัติเต็มรูปแบบของ micro-ORM เนื่องจากสามารถดำเนินการ CRUD ผ่าน “Raw SQL” นอกจากนี้ยังรองรับคุณสมบัติพิเศษของ full-ORM
ลองดูตัวอย่างข้องการ execute Raw SQL
// Queryusing (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ connection.ExecuteQuery<Person>("SELECT * FROM [Person] WHERE Id = @Id;", new { Id = 10045 });}
// Insertusing (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ var entity = new { Id = 10045, FirstName = "John", LastName = "Smith", LastUpdatedUtc = DateTime.UtcNow }; var affectedRows = connection.ExecuteNonQuery("INSERT INTO [Person] (Id, FirstName, LastName, LastUpdatedUtc, CreatedDateUtc) " + "VALUES (@Id, @FirstName, @LastName, @LastUpdatedUtc, GETUTCDATE());", entity);}
// Updateusing (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ var entity = new { Id = 10045, FirstName = "John", LastName = "Smith", LastUpdatedUtc = DateTime.UtcNow }; var affectedRows = connection.ExecuteNonQuery("UPDATE [Person] SET FirstName = @FirstName, LastName = @LastName, LastUpdatedUtc = @LastUpdatedUtc " + "WHERE Id = @Id;", entity);}
// Deleteusing (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ var affectedRows = connection.ExecuteNonQuery("DELETE FROM [Person] WHERE Id = @Id;", new { Id = 10045 });}หรือจะใช้แบบการเรียก method-based
// Queryusing (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ var person = connection.Query<Person>(p => p.Id == 10045).First();}
// Insertusing (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ var person = new Person { FirstName = "John", LastName = "Smith", LastUpdatedUtc = DateTime.UtcNow, CreatedDateUtc = DateTime.UtcNow }; var personId = connection.Insert(person);}
// Updateusing (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ var person = connection.Query<Person>(p => p.Id == 10045).First(); person.FirstName = "John (Updated)"; person.LastName = "Smith (Updated)"; person.LastUpdatedUtc = DateTime.UtcNow; var updatedRows = connection.Update(person);}
// Deleteusing (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ var deletedRows = connection.Delete<Person>(p => p.Id == 10045);}ฟีเจอร์อื่นๆ ของ ORM แบบอื่นยังมีอยู่ในไลบรารีนี้ผ่านการเรียกใช้ตามวิธีการ (เช่น BatchQuery, BulkInsert, Delete, DeleteAll, Insert, InsertAll, Update, UpdateAll, Merge, MergeAll เป็นต้น)
Batch Operations
การดำเนินการแบบแบตช์ในไลบรารีนี้เป็นคำสั่งแบบแพ็กทั้งหมด โดย DbCommand เดียวใช้เพื่อดำเนินการคำสั่ง SQL หลายรายการในครั้งเดียว กระบวนการนี้เป็น ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) โดยค่า default chunk คือ 10 records ลองดูตัวอย่างด้านล่าง
// Create a listvar orders = new List<Order>();
// Add each itemorders.Add(new Order { CustomerId = 10045, Quantity = 1, ProductId = 24 });orders.Add(new Order { CustomerId = 10045, Quantity = 4, ProductId = 27 });
// More orders here
// Call the InsertAllusing (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ connection.InsertAll<Order>(orders);}Bulk-Operations
ในทางกลับกัน การดำเนินการจำนวนมากใช้ (bulk-operations) ที่ ADO.NET ให้บริการ ตามค่าเริ่มต้น ไลบรารีกำลังใช้คลาส SqlBulkCopy เพื่อดำเนินการ bulk-insert ไปยัง Database ลองดูตัวอย่างด้านล่าง
// Create the listvar orders = new List<Order>();
// Add each itemorders.Add(new Order { CustomerId = 10045, Quantity = 1, ProductId = 24 });orders.Add(new Order { CustomerId = 10045, Quantity = 4, ProductId = 27 });
// More orders here
// Call the BulkInsertusing (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ connection.BulkInsert<Order>(orders);}Replicating Big Data via BulkInsert
เรายังสามารถนำมา Replicating Big Data จาก soource ไปอีก source ได้ด้วย ลองดูตัวอย่างด้านล่าง
// Variables for pagingvar lastId = 10000;var batchSize = 1000000;var page = 1;
// Create a source connection (Oracle)using (var sourceConnection = new OracleConnection(sourceConnectionString)){ // Read the data with target columns using (var reader = sourceConnection.ExecuteReader("SELECT Id, FirstName, LastName, LastUpdatedUtc, DateInsertedUtc FROM [dbo].[Person] WHERE Id > @Id OFFSET @Offset FETCH NEXT @BatchSize ROWS ONLY;", new { Id = lastId, Offset = (batchSize * page), BatchSize = batchSize })) { // Create a destination connection (SqlServer) using (var destinationConnection = new SqlConnection(destinationConnectionString)) { // Call the BulkInsert by passing the reader var insertedRows = destinationConnection.BulkInsert("Person", reader); } }}Note: อันนี้ยังไม่ได้ทดสอบ :)
Executing a Stored Procedure
เรายังสามารถเรียก Stored Procedure ได้ด้วย ยกตัวอย่างว่าเรามี sp_get_customer_orders ที่ Database
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_get_customer_orders]( @CustomerId INT)ASBEGIN SELECT * FROM [dbo].[Orders] WHERE (CustomerId = @CustomerId) ORDER BY OrderDateUtc ASC;ENDดังนั้นเราก็จะเรียกได้ดังนี้
using (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)){ var orders = connection.ExecuteQuery<Order>("[dbo].[sp_get_customer_orders]", new { CustomerId = 10045 }, commandType: CommandType.StoredProcedure);}ขอจบตอนแรกไว้เท่านี้ก่อน แล้วเจอกัน